E-Business PLR
Your First Guide to Google Ads – Beginners Guide
Introduction: Why Google Ads?
Imagine you own a small, charming bakery called “The Sweet Corner.” You bake the most delicious croissants and the most beautiful custom cakes in your city. The problem is, how do people who are looking for exactly that find you? They might walk past your shop by chance, or hear about you from a friend. But what if you could place a sign right in front of them the exact moment they thought, “I need a great birthday cake”?
That, in essence, is the magic of Google Ads.
In today's digital world, when people have a question or a need, their first instinct is to “Google it.” They search for everything from “best pizza near me” to “how to fix a leaky faucet” to “online data science courses.” These searches are not just questions; they are expressions of intent, need, and desire. Google Ads allows you to place your business directly in front of these motivated individuals, at the very moment they are looking for a solution you provide.
What is the Difference Between Google Ads (SEM) and SEO?
You may have heard of SEO, or Search Engine Optimization. It’s crucial to understand the difference.
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): This is the practice of improving your website to “earn” a free spot in Google's search results. It involves creating high-quality content, ensuring your site is technically sound, and building authority over time. SEO is a long-term strategy—a marathon, not a sprint.
- Google Ads (a part of SEM – Search Engine Marketing): This is the practice of paying to have your website appear in the sponsored results on Google. The results are nearly instant—you can start getting visitors to your site the same day you create your campaign. It's a sprint that gives you immediate visibility.
The best marketing strategies use both. SEO builds a sustainable, long-term foundation of trust and authority, while Google Ads provides immediate, targeted traffic and valuable data. For a beginner, Google Ads is the fastest way to get in the game.

A Few Key Terms to Get You Started
The world of digital advertising has its own language, but don't be intimidated. Here are the five most important terms you'll need to know right away.
- Impression: An impression happens each time your ad is shown on the search results page.
- Click: A click is when a user is interested enough in your ad to click on it and visit your website.
- CPC (Cost-Per-Click): This is the amount you pay Google each time someone clicks on your ad.
- CTR (Click-Through Rate): This is a percentage that shows how often people who saw your ad ended up clicking it. It’s calculated as
(Clicks ÷ Impressions) x 100. - Conversion: This is the ultimate goal. A conversion is any valuable action a user takes on your website after clicking your ad.
Now that you understand the “why,” let's move on to the “how.”
Chapter 1: Getting Started – Setting Up for Success
This chapter will walk you through creating your account, understanding its basic layout, and organizing it properly from day one.
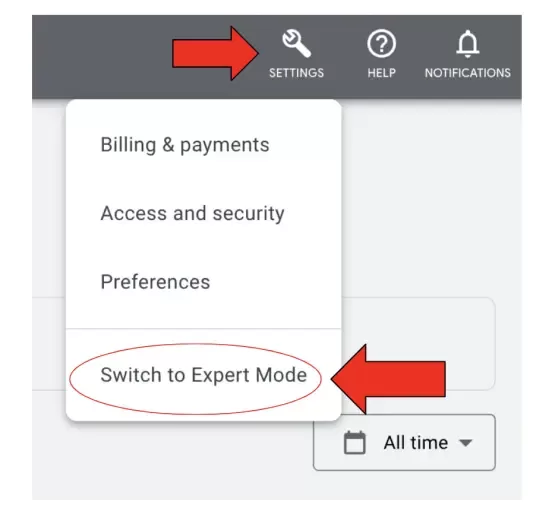
Step 1: Create Your Account (and Switch to Expert Mode!)
First, go to ads.google.com and click “Start Now.”
CRITICAL ADVICE: Google will try to guide you into a simplified experience called “Smart Mode.” We want to be in control. As you are setting up your account, look for a small link that says “Switch to Expert Mode.” Click it immediately.
Step 2: A Quick Tour of the Google Ads Dashboard
When you first log in, the dashboard can look overwhelming. You only need to know about a few key areas for now:
- The Left-Hand Navigation Menu: This is your command center where you will see
Campaigns,Ad Groups,Keywords, etc. - The Top Bar: This bar contains important tools like
Tools & Settings(the wrench icon) andReports.
Step 3: Understanding the Account Structure
Proper organization is the secret to a successful Google Ads account. Imagine it's a filing cabinet.
- The Account (The Filing Cabinet)
- Campaigns (The Drawers)
- Ad Groups (The Folders)
- Keywords and Ads (The Documents)
- Ad Groups (The Folders)
- Campaigns (The Drawers)
This structure (Account > Campaign > Ad Group > Keywords/Ads) is the key to relevance, which Google rewards with better ad positions and lower costs.


Step 4: Setting Up Your Billing
Go to Tools & Settings > Billing > Summary to set this up. You will need to add a payment method to allow your ads to run.
With your account created and the basic structure understood, you are now ready for the fun part: planning the campaign.
Chapter 2: The Foundation of Every Great Campaign
A successful campaign begins with a clear plan. In Google Ads, that foundation is your goals, your audience, and your keywords.
1. Defining Your Advertising Goals What do I want to achieve with these ads? A specific, measurable goal is key. For our bakery, “The Sweet Corner,” our goal is: To get at least 10 new orders for custom cakes per month through our website's contact form.
2. Understanding Your Target Audience Who are you trying to reach? Think about your ideal customer: parents planning a party, couples looking for a wedding cake, etc. This helps you write ads that speak directly to them.
3. Keyword Research for Beginners Keywords are the bridge between a search and your ad.
Using the Google Keyword Planner In your account, go to Tools & Settings > Planning > Keyword Planner. Select “Discover new keywords” and enter your ideas. The tool will give you new keyword ideas, their monthly search volume, and estimated cost.
Understanding Keyword Match Types
- Exact Match:
[custom wedding cake]– Most control. - Phrase Match:
"custom wedding cake"– A balance of control and reach. - Broad Match:
custom wedding cake– Least control, avoid for now.
The Power of Negative Keywords Tell Google what keywords not to target. For our premium bakery, we would add negative keywords like -cheap, -free, and -recipe to avoid wasting money.
Chapter 3: Creating Your First Search Campaign
Let's walk through the step-by-step process of launching your campaign.
From your dashboard, click the big blue “+” button and select “New campaign.”
[Slika: Snimka zaslona dijela Google Ads sučelja s plavim '+' gumbom i padajućim izbornikom na kojem je odabrano 'New campaign'.]
1. Choose Your Objective & Campaign Type Choose “Leads” as your objective and “Search” as your campaign type.
2. Campaign Settings
- Networks: Uncheck the “Display Network.” This is very important for a beginner's Search campaign.
- Locations: Be specific! Target only the city or area you serve.
3. Writing Ads That Get Clicks This is what the user sees. Make it compelling.
“Before & After” Ad Copy Example:
4. Using Ad Extensions Extensions make your ad bigger and more useful. Use them!
- Sitelink Extensions: Add links to specific pages (e.g., “Our Flavors,” “Contact Us”).
- Callout Extensions: Highlight benefits (e.g., “Free Consultation,” “5-Star Rated”).
5. Review and Launch Review the summary of your campaign. If it all looks good, hit “Publish campaign.” Congratulations!
Chapter 4: Beyond Search – A Quick Look at Display Ads
Display ads are visual banner ads that appear on millions of websites and apps. They are great for building brand awareness and for remarketing (targeting previous website visitors).
For now, focus on mastering your Search campaigns. But keep Display ads in mind for the future.
Chapter 5: Are Your Ads Working? Measuring What Matters
How do you know if you are spending money wisely? The answer is Conversion Tracking.
What is Conversion Tracking? It connects your ad clicks to valuable actions on your website (like a purchase or a form submission). Without it, you are flying blind.
A Simplified Guide to Setting Up a Conversion
- In Google Ads, go to Tools & Settings > Measurement > Conversions.
- Click the blue “+” to create a new conversion action.
- Select “Website.”
- Follow the steps to get your Google Tag, a piece of code to add to your website.
Understanding the Key Metrics (Now with Context) Once tracking is set up, you can see the full story in your reports.
- Conversions: The total number of valuable actions completed.
- Cost per Conversion (Cost / Conversions): How much you paid for each lead or sale.
- Conversion Rate (Conversions ÷ Clicks) x 100: The percentage of clicks that turned into customers.
Chapter 6: Next Steps – The Journey of Optimization
You should never “set it and forget it.” Optimization is the ongoing process of improving your campaigns.
1. Review the Search Terms Report Go to Keywords > Search Terms. This report shows you the actual search queries people typed. Use it to find new keywords and, more importantly, to add irrelevant searches as negative keywords.
2. Check on Your Ads Pause ads with low CTR and write new ones based on what you learn from your best-performing ads.
3. Adjust Your Bids Lower bids on expensive, low-performing keywords. Increase bids on profitable keywords to get more traffic.
The Importance of Patience Do not make changes every day! Give the algorithm time to learn (at least a week).
Conclusion
You've come a long way. The key takeaways are:
- Start with a clear goal.
- Structure is everything.
- Keywords are the bridge to your customers.
- Conversion tracking is not optional.
- Optimization is a continuous process.
You now have the fundamental knowledge to connect your business with the right person at the right time. Your next customer is just a search away.
Glossary
- Ad Group: A container for related keywords and ads.
- Ad Rank: A value that determines your ad position.
- Campaign: The highest level of organization, with its own budget and settings.
- Conversion: A valuable action a customer takes on your website.
- Cost-Per-Click (CPC): The amount you pay for a single click.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The percentage of impressions that resulted in a click.
- Keyword: A word or phrase you target.
- Negative Keyword: A word or phrase that prevents your ad from showing.
- Quality Score: A 1-10 score on the quality and relevance of your keywords and ads.
- SEO: Search Engine Optimization (earning free traffic).
- SEM: Search Engine Marketing (includes paid ads and SEO).


